Histidine requirements of broilers for protein synthesis and beyond
2020년 08월 25일
- Broiler
- Function
- Low CP
Behnam Saremi
CJ Europe GmbH
INTRODUCTION
Reducing emission across a variety of industries has been the focus for years. Global warming and climate change have shifted part of the focus to the agriculture. Thus, agriculture and specifically animal production is under pressure to reduce nitrogen and phosphorus emissions and reduce gaseous pollutions such as CO2 and methane. Phytase has been used for decades to reduce phosphorus excretion and to increase phytate phosphorus availability to the animals. To reduce the nitrogen emissions, modern monogastric diets have switched from protein optimization to amino acid optimization. Lysine, methionine, threonine, tryptophan, and valine are commonly used in feed formulations. Isoleucine and arginine have been recently introduced to the market as supplementary amino acids. Based on these, the industry is designing low protein and functional diets to contribute in reducing the impact of animal production on environmental pollution. Histidine (His) is the next limiting amino acid which is already registered and used in parts of the world in EU. Herein, the role of His and its requirements in monogastric species is explained.
Histidine requirements in broilers
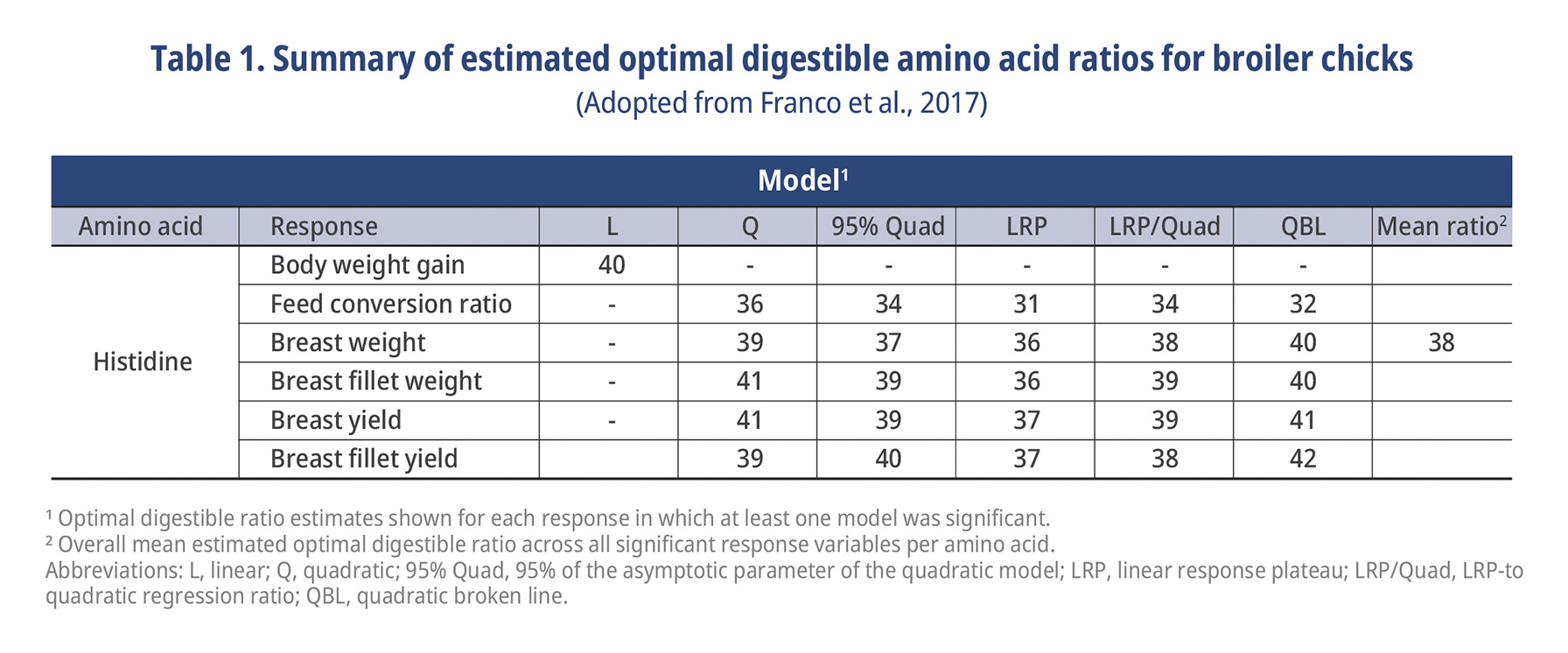
The His requirement for maximum weight gain and feed efficiency is determined to be not more than 0.31% (8-22 days post hatch) in broiler's diet in which the His digestibility was determined to be 81.4% (Han et al. 1991). The optimal ratios of digestible His (dHis) to digestible Lys (dLys) for starter phase in the literature are 27% (Dean and Scott, 1965), 32% (Huston and Scott, 1968), 36% (Sasse and Baker, 1973), 36% (Baker and Han, 1994), and 36% (Dorigam et al., 2013). Wecke and Liebert (2013) summarized results of 12 experiments and ended up in a His to Lys ratio (His/Lys) of 344. The most recent study on His requirement in broilers was conducted by the Dilger research laboratory and published by Franco et al. (2017) at the University of Illinois. On average a His/Lys of 38% was reported and they also observed a higher His requirement for carcass parameters as compared with body weight and FCR in 8 to 17 days old birds (Table 1). Broiler breeder companies (ROSS and COBB) currently do not have His recommendations. Brazilian tables suggest 37% His/Lys for all ages of broilers. Same tables suggest dHis requirements of 0.49, 0.48, 0.46, 0.40, and 0.36% for 1-7, 8-21, 22-33, 34-42, and 43-46 days of age for high performing broilers (Rostagno et al. 2017).
In a typical corn soybean broiler feed diet, His/Lys is around 43% (starter phase) under a normal protein level (21.7% CP). An attempt to reduce the protein content down to 20% would reduce the His/Lys to 38%. Thus, after arginine and isoleucine, histidine would be the next limiting amino acid in corn soybean diets. In a wheat corn soybean diet, His/Lys starts from 40% in a normal protein condition and a similar attempt to reduce crude protein would cause an isoleucine, leucine and glycine plus serine deficiency as well as drop of His/Lys to below 38%. These are some examples showing the importance of His under different formulation conditions.
Physiological roles of histidine
Histidine is an integral component of a broad set of tissues including skin, feather, bone, ligaments, and obviously muscle (NRC, 1994). This amino acid also serves to stimulate the digestive secretion of gastrin, a hormone that activates production of hydrochloric acid and pepsinogen, which are essential for digestion of dietary protein (Berdanier, 1998; DMello, 2003).
Histidine together with β-alanine are needed for carnosine synthesis which is a dipeptide synthesized by the carnosine synthase. High concentration of carnosine is found in muscle and brain tissues, especially in breast muscle of mammalian and avian species (Kohen et al., 1988; ODowd et al., 1988; Biffo et al., 1990). Recently, carnosine has gained increasing attention as a functional ingredient for human food because of its high antioxidant activity (Mozdzan et al., 2005), high buffering capacity to maintain intracellular pH change (Abe, 2000), and anti-glycating and anti-aldehyde effects (Aldini et al., 2005; Guiotto et al., 2005).
Histidine supplementation in broiler diets increases the concentration of carnosine in breast muscle of 1-32 days old broilers (Park et al., 2013). To increase concentration of carnosine in breast muscle tissue of broilers using L-His or spray dried blood cells (SDBC, a His-rich raw material), only the L-His supplemented diet could increase the concentration of carnosine and improved the antioxidative status of breast muscle (Kopec et al., 2013). Whereas, the spray dried blood cells caused a loss in performance parameters probably because of a very high leucine concentration in SDBC contrary to L-His which improves performance.
Breast muscle has about 3 times higher carnosine concentration than thigh muscle (Barbaresi et al., 2019). Moreover, slow growing chickens presented higher carnosine concentration in breast muscle compared with ROSS 308 (ad libitum fed or limited fed) (Barbaresi et al., 2019). Recently, concentration of carnosine is also linked to the incidence of breast muscle diseases (Soglia et al., 2019). Severe cases of breast gaping presented a low concentration carnosine. Thus, there is a potential in His to help the industry solving similar issues. Having in mind that some of the nutritional trends of last decades has been ban of animal protein sources (meat and bone meal and blood meal) and lowering the concentration of protein in the diets both of which has dramatically reduced the concentration of histidine in feed formulations.
Conclusion
Histidine is getting a fresh attention in broiler nutrition as the next limiting amino acid. New nutritional trends had tremendously reduced concentration of His in broilers diet. CP reduction has urged the need of crystalline His for commercial broiler diets. Histidine is a functional amino acid with antioxidative properties. As described above, it can influence yield and carnosine concentration of broilers breast filets and thus nutritionists and formulators of broiler diets should balance for His not only to meet nutritional requirements but also to benefit from functional aspects of His as a new solution available on the market.
























































