Methyl donor requirement will increase by addition of Guanidinoacetic acid to diets
2020년 11월 30일
- Function
- L-Met
- Metabolism
Behnam Saremi
CJ Europe GmbH
Creatine is needed for energy homeostasis in muscle tissues. Creatine preserves ATP energy in the form of creatine phosphate a compound which will release its energy when there is an immediate basic source of energy like ATP needed. For example, in cases of fight or flight in wild animals or aerobic intensive exercise free ATP would not be sufficient to cover immediate energy needs. Therefore, creatine phosphate would release its energy to cover such sudden energy needs.
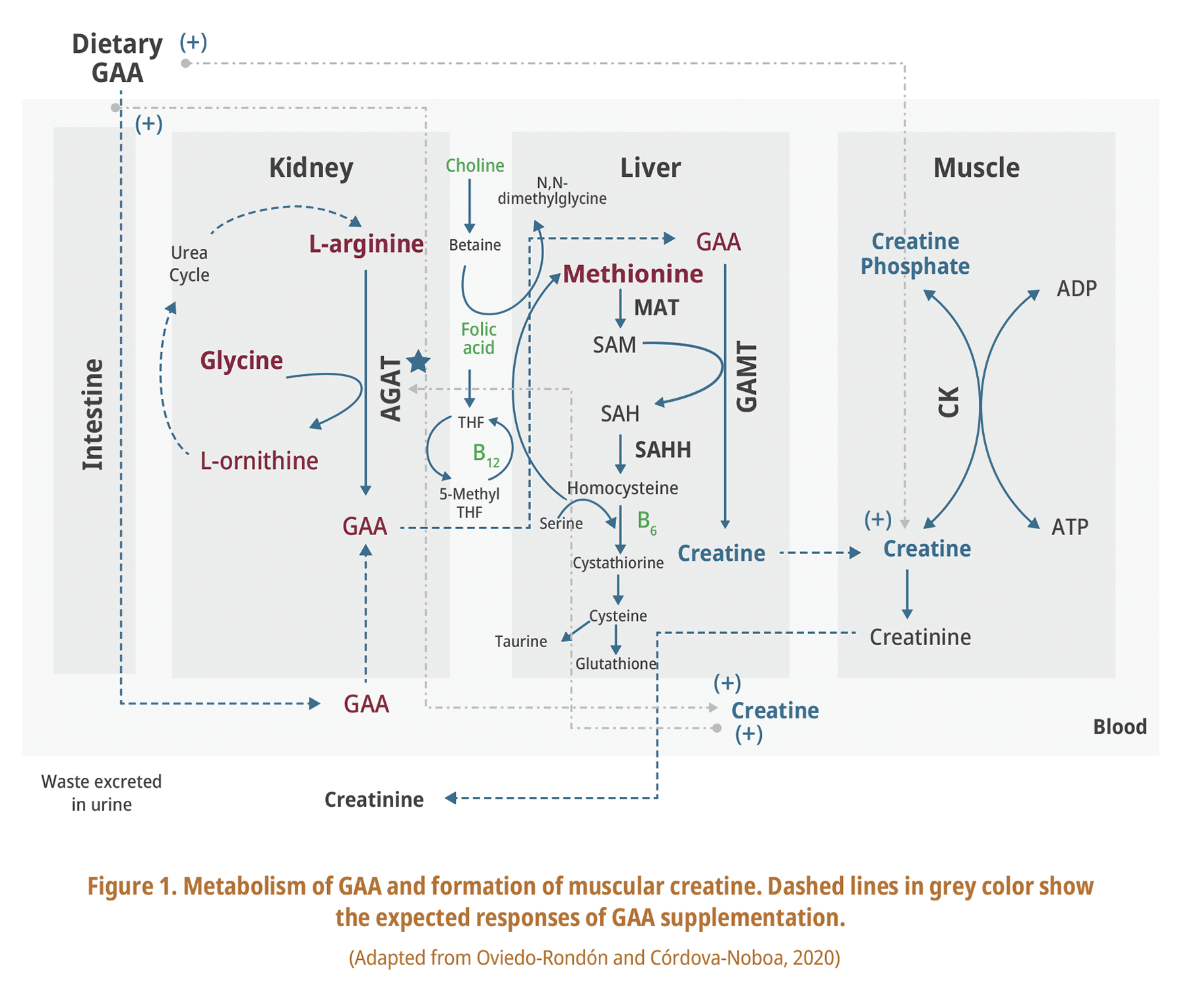
Creatine synthesis is a very simple process involving just two enzymes. It does, however, require three amino acids: arginine, glycine, and methionine. Arginine:glycine amidinotransferase (AGAT) transfers an amidino group from arginine to the amino group of glycine to produce guanidinoacetate (GAA) and ornithine in the kidney (Fig. 1). GAA is transported to liver where methyltransferase (GAMT) employs S-adenosylmethionine (SAM) to methylate GAA, producing creatine and S-adenosylhomocysteine (SAH). Creatine is transported to muscle tissues where it can be phosphorylated to creatine phosphate. Creatine synthesis may consume as much as 6377% of all of the labile methyl groups used by piglets (Bosnan et al. 2009).
Methionine is an essential amino acid which is needed for critical physiological mechanisms such as initiation of protein synthesis, methylation, etc. Among others, methionine is also needed for methylation including methylation of GAA to creatine. Methionine acts as a methyl donor through conversion of SAM to SAH. Methionine used for creatine synthesis is ~30.4% of methionine deposited in protein (Bosnan et al. 2009).
GAA is commercially available and is sold to the feed and premix industries with major claims of energy and arginine sparing effects. The recommended dose of GAA is mentioned to be either 600 or 1200 grams per ton of feed based on a 77% arginine sparing claim (arginine equivalent of 0.46 or 0.92 g/kg of feed, respectively). However, the exact dose of GAA is not clear according to EFSA (2009). GAA addition to feed can spare some arginine because high GAA concentration send a negative feedback to AGAT enzyme to reduce the activity of this enzyme. Thus, the arginine used for an endogenous GAA synthesis will be spared and theoretically will be available for other physiological purposed. AGAT is a rate limiting enzyme determining how much creatine is needed in muscle tissues thus how much GAA is needed to be synthesized in kidney. Currently, there is no data demonstrating the minimum amount of GAA needed to reduce AGAT activity. Therefore, an eventual extra load of GAA through feeding a supplementary GAA will increase the utilization of methyl donors to methylate the extra GAA because GAMT enzyme has no control on the methylation step and most of GAA will be methylated to creatine if not excreted through urine.
Increasing dietary GAA intake increases fecal and renal GAA, creatine, and creatinine excretion (Tossenberger et al. 2016). Considering renal GAA excretions, true availability of supplemental GAA will be reduced with increasing dose of GAA (83% vs. 71% for 0.6 vs. 6 g GAA per kg of feed, respectively). Taking into account renal creatine and creatinine excretions, as they are a consequence of increasing dietary GAA supply, true availability of supplemental GAA shrank from 76% (0.6 g GAA per kg feed) to 46% (6.0 g GAA per kg of feed) (Tossenberger et al. 2016). Thus, accurate determination of an effective dose of GAA to reduce the AGAT activity is important otherwise an extra unnecessary inclusion of GAA will soak up the methyl donors including methionine which means not being available for other physiological purposed or for growth. Knowing arginine as a cost-effective amino acid as compared with GAA, we should let the animal enzymatic machinery to decide about the amount of GAA needed to be synthesized from arginine without interfering with the normal physiological processes by means of adding GAA to stop AGAT enzyme.
Recently EFSA has published a new opinion (2016) about GAA safety where the role of methyl donors in animals fed with supplementary GAA is taken into a serious consideration. EFSA considers 600 to 1200 grams of GAA as safe considering that the diets are sufficiently supplemented with methyl donors such as choline chloride, vitamin B12 and folic acid. However, the absolute requirement of animals for methyl donor groups is not well defined creating a critical situation and an uncertainty if these requirements are really met.
In conclusion, arginine is a straightforward amino acid and a cost-efficient supplementary source to fulfill the arginine requirements. GAA application in feed can create complications in accurate fulfillment of arginine requirement of animals. The hidden costs associated with GAA such as a higher demand for methyl donors is another reason to be considered when nutritionists decide about how to fulfill the arginine requirements of pigs and poultry.